Collider
Colliders can be used to define the shape of the object that needs to be physically collided with, and different geometries have different properties. Colliders are usually classified as follows:
- Basic Colliders. The common ones include Box, Sphere, Cylinder, Cone and Capsule.
- Composite Colliders. You can easily simulate game object shapes by adding one or more base colliders to a node, while keeping the performance overhead low.
- MeshCollider. Generate colliders based on object mesh information, fully fitting the mesh.
- SimplexCollider. Provide point, line, triangular surface, tetrahedron collision.
- PlaneCollider. Can represent an infinite plane or half-space. This shape can only be used for static, non-moving objects.
- TerrainCollider. A special support for concave terrain.
NOTE: In some (e.g. Bullet) physics backends, very high scaled sizes should be avoided due to floating point inaccuracy, here it is recommended to be below 1000. e.g. a certain box collider with a Y value of 40 and a Z value of 0.01 for its Size property, at this point they have a Y, Z ratio of more than 1000, at which case there may be inaccurate floating point calculations.
Add Collider Component
Here we will take the example of adding BoxCollider component.
Add via Editor
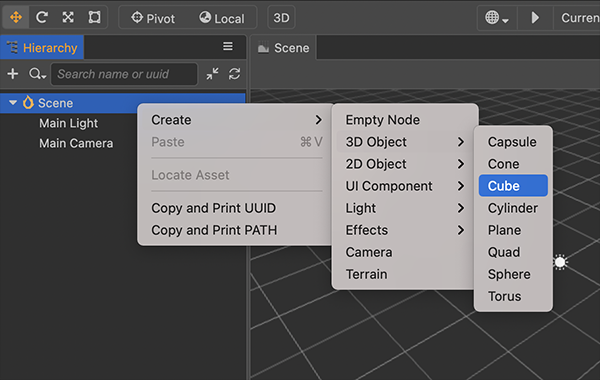
Create a new 3D object Cube, click the + Create button in the top left corner of Hierachy panel, then select Create -> 3D Object -> Cube.
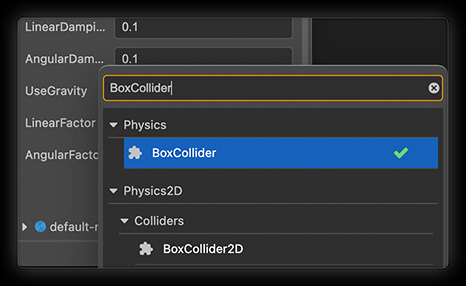
Select the Cube created in Hierachy panel, click the Add Component button at the bottom of the Inspector panel on the right, and select Physics -> BoxCollider to add a collider component.
Add by Code
import { BoxCollider } from 'cc'
const boxCollider = this.node.addComponent(BoxCollider);Collider Common Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Attached | The Rigidbody to which the collider is attached |
| Material | The Physics Material used by the collider, or the engine's default physics material if not set |
| IsTrigger | Whether or not it is a Trigger, the trigger will not generate physics feedback |
Please note the following points for getting rigid body.
- This attribute returns
nullif the node itself does not have aRigidBodycomponent. - The real attribute corresponding to Attached is called
attachedRigidBody, which is a read-only attribute and cannot be modified.
let collider = this.node.addComponent(BoxCollider)!;
let rigidbody = collider.attachedRigidBody;To editing Colliders, please refer to: Collider Gizmo.
Note: Please check Different physical back-end collision shape support before using colliders to make sure the physics engine you are currently using supports it.
Colliders
Basic Colliders
BoxCollider
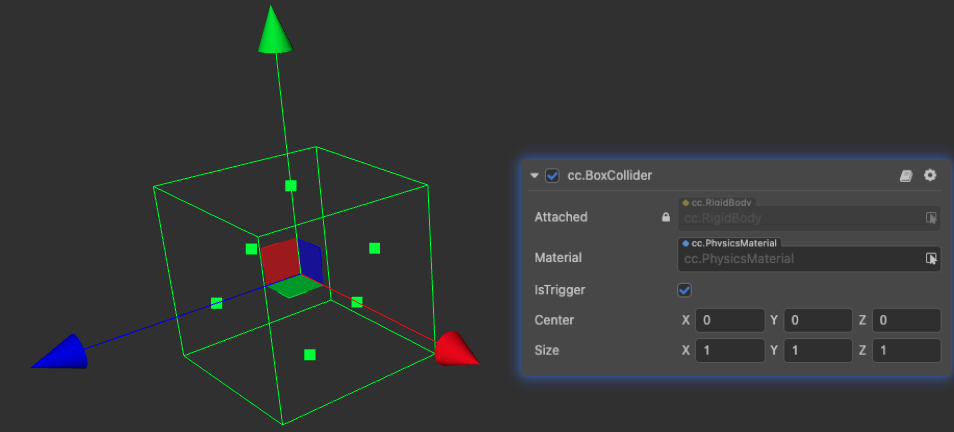
The BoxCollider is a rectangular shape based collider that can be used to achieve collision of wooden boxes, walls, and other objects. It can be used to combine into composite shapes.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Center | The center of the shape in the local coordinate system |
| Size | The size of the box in the local coordinate system, i.e. length, width and height |
Please refer to BoxCollider API for details.
SphereCollider
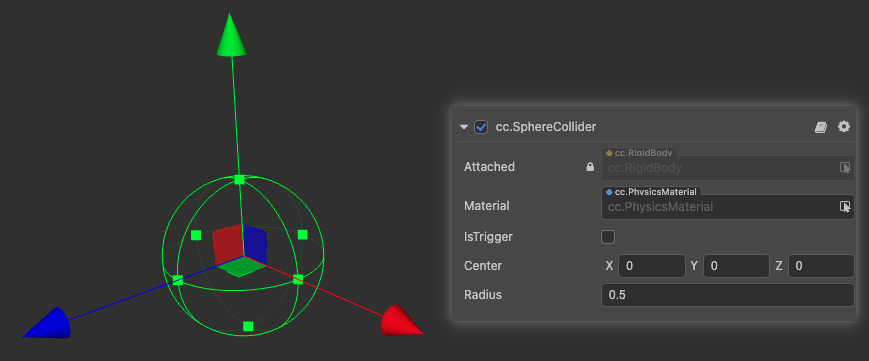
SphereCollider is a sphere-based collider.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Center | The center of the shape in the local coordinate system |
| Radius | The radius of the sphere in the local coordinate system |
Please refer to SphereCollider API for details.
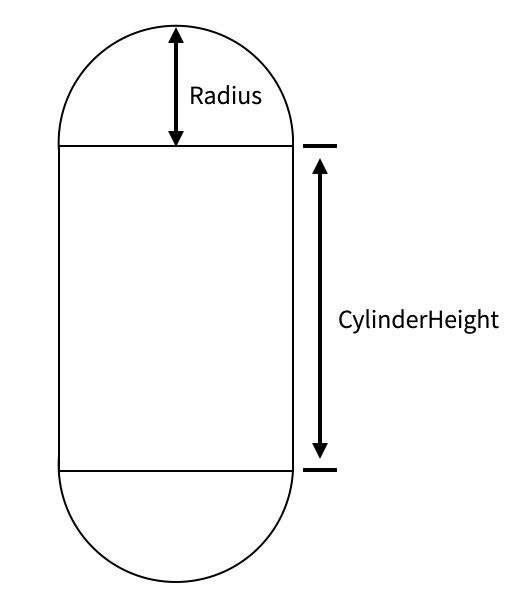
CapsuleCollider
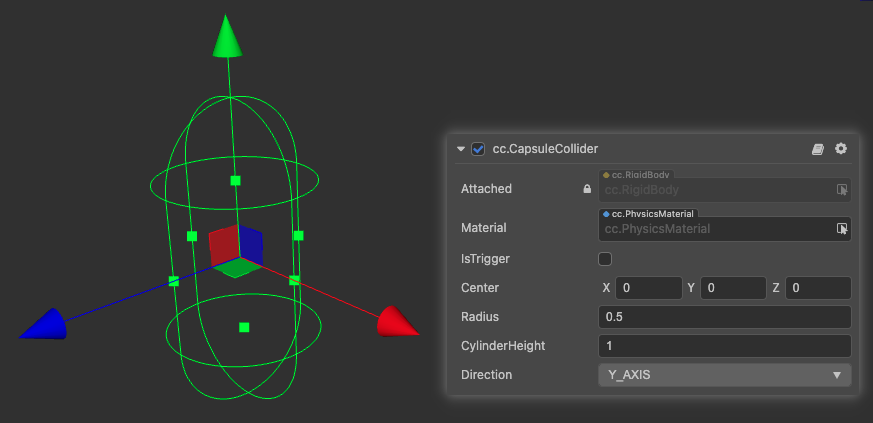
CapsuleCollider is a collider based on the shape of a capsule.
Note:
cannon.jsdoes not support capsule components, it is recommended to use two spheres and a cylinder to collocate.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Center | The center of the shape in the local coordinate system |
| Radius | The radius of the sphere on the capsule in the local coordinate system |
| CylinderHeight | The height of the cylinder on the capsule in the local coordinate system |
| Direction | The orientation of the capsule in the local coordinate system |
Please refer to CapsuleCollider API for more details.
CylinderCollider
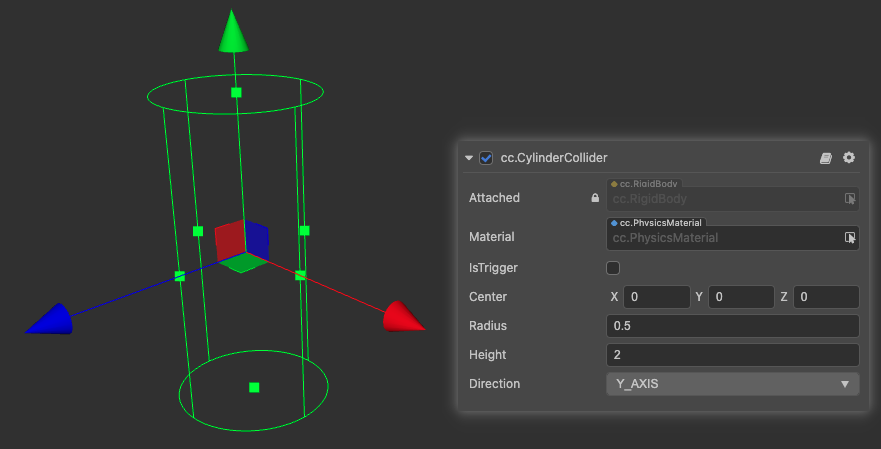
CylinderCollider is a cylinder-based collider.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Center | The center of the shape in the local coordinate system |
| Radius | The radius of the circle on the cylinder in the local coordinate system |
| Height | The height of the cylinder in the local coordinate system in the corresponding axial direction |
| Direction | The orientation of the cylinder in the local coordinate system |
Please refer to CylinderCollider API for details.
ConeCollider
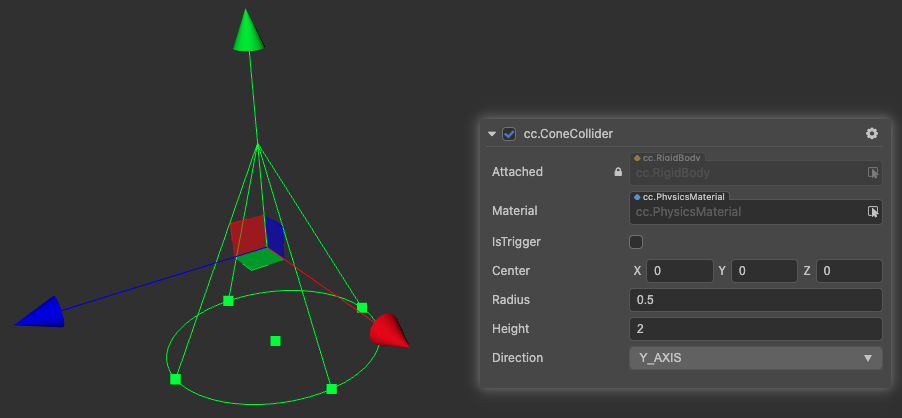
ConeCollider is a collider based on a cone.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Center | The center of the shape in the local coordinate system |
| Height | The height of the cone in the local coordinate system in the corresponding axis |
| Direction | The orientation of the cone in the local coordinate system |
Please refer to ConeCollider API for details.
Composite Colliders
A composite collider is not a single collider component type, but a combination of multiple base colliders that can easily simulate the shape of complex game objects.
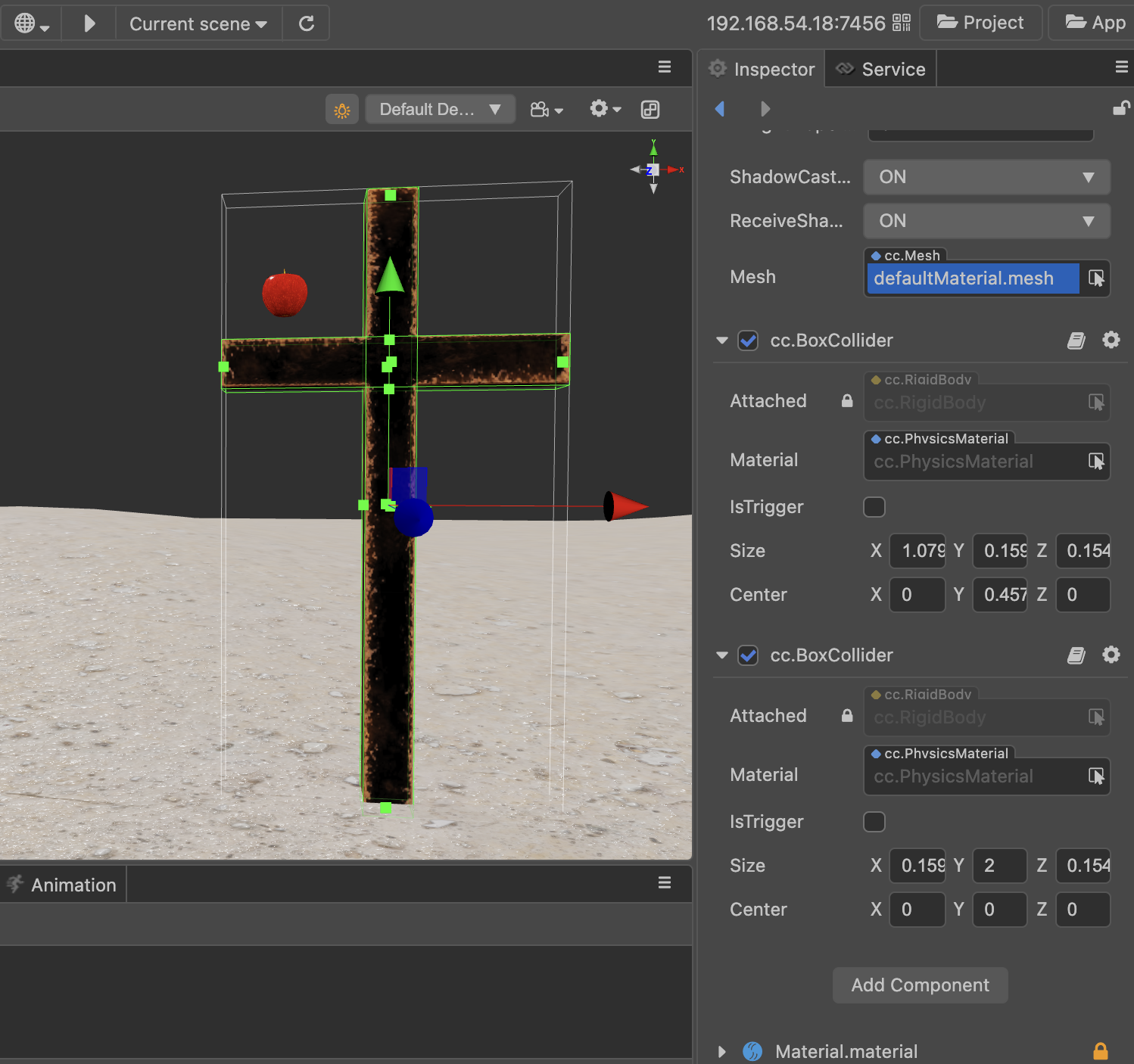
PlaneCollider
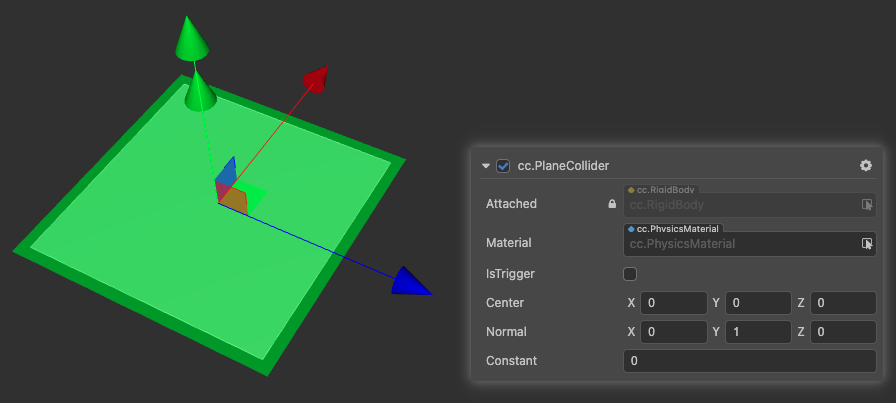
PlaneCollider is a collider that belongs to a planar model. Planes can be created by right-clicking Create -> 3D Objects -> Plane in the Hierarchy panel.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Center | The center of the shape in the local coordinate system. |
| Normal | The normal of the plane in the local coordinate system. |
| Constant | The distance of the plane from the origin along the normal in the local coordinate system |
Please refer to PlaneCollider API for details.
MeshCollider
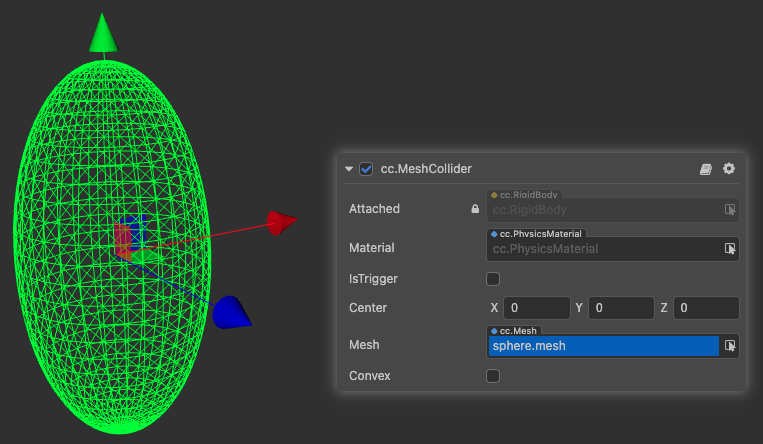
MeshCollider is a collider based on the model mesh.
Notes:
cannon.jshas poor support for mesh collider components, allowing detection with only a few colliders (spheres, planes).- Convex functionality is currently only supported in the
ammo.jsbackend.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Center | The center of the shape in the local coordinate system |
| Mesh | The mesh resource used by the mesh collider to initialize the mesh collider |
| Convex | Whether to use the convex packet approximation of the mesh instead, the number of mesh vertices should be less than 255, and the kinetics can be supported when turned on |
MeshCollider interface please refer to MeshCollider API.
SimplexCollider
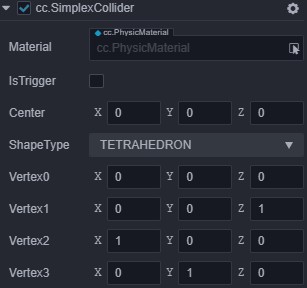
SimplexCollider is a point, line, face and tetrahedron based collider.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Center | The center of the shape in the local coordinate system |
| ShapeType | The pure shape type, including four types: point, line, triangle, and tetrahedron |
| Vertex0 | The vertex 0 of a pure shape, the point (consisting of 0) |
| Vertex1 | vertex 1 of a simplex, line (composed of 0, 1) |
| Vertex2 | vertex 2 of a pure form, triangles (and so on) |
| Vertex3 | Vertex 3 of a pure form, tetrahedron |
Please refer to SimplexCollider API for the interface to the simplex collider component.
Note:
cannon.jssupport for lines and triangles is currently imperfect.
TerrainCollider
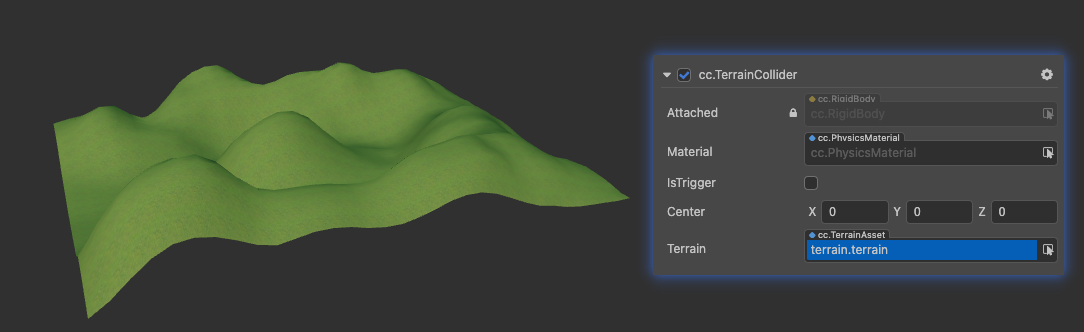
TerrainCollider is a collider generated by a terrain surface, with the same specific shape as the object it is attached to in the Terrain asset.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Center | The center of the shape in the local coordinate system |
| Terrain | Gets or sets the terrain asset referenced by this collider |
See TerrainCollider API for the Terrain Collider component interface.
Auto Scaling
Each component is bound to a node, and some components will dynamically update data based on the bound node. Among them, the collider component will automatically update the corresponding shape data based on the node information, so that the collider can fit the rendered model more closely. Take the model component as an example.
The model component will automatically update the model's world matrix based on the bound nodes, thus enabling changes to the node's position, scaling, rotation, and other information, which can make the rendered model have the corresponding affine transformation.
However, there are some properties of colliders that cause scaling to be handled less differently.
- Colliders are generally described in terms of geometric structures
- Colliders are mostly of convex packet type
These properties restrict transformations such as tangent, non-uniform scaling, etc. Take the sphere as an example.
Assuming that the scaling information of the bound node is (1,2,1) (non-uniform scaling), since the model and the collider describe different structures, the sphere model uses multiple base elements (such as triangular surfaces) to describe, and after scaling will be shaped into a pebble-like shape; while the sphere collider is described according to the radius size, scaling will take the dimension with the largest value to scale the radius (this is to encircle the model as much as possible with the collider), but it is still a sphere after scaling, so it cannot precisely encircle the pebble-like size of the sphere model.
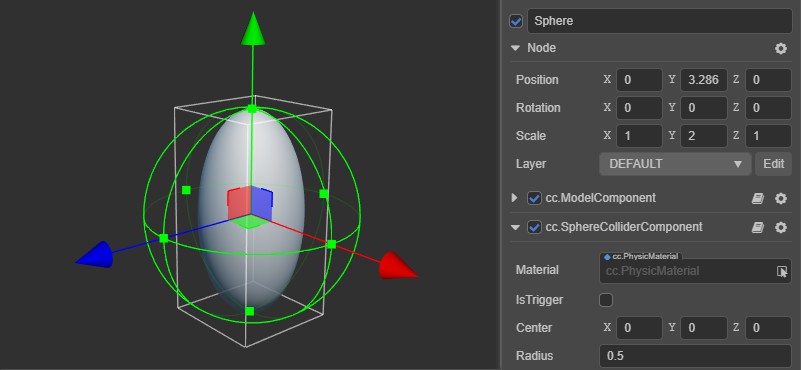
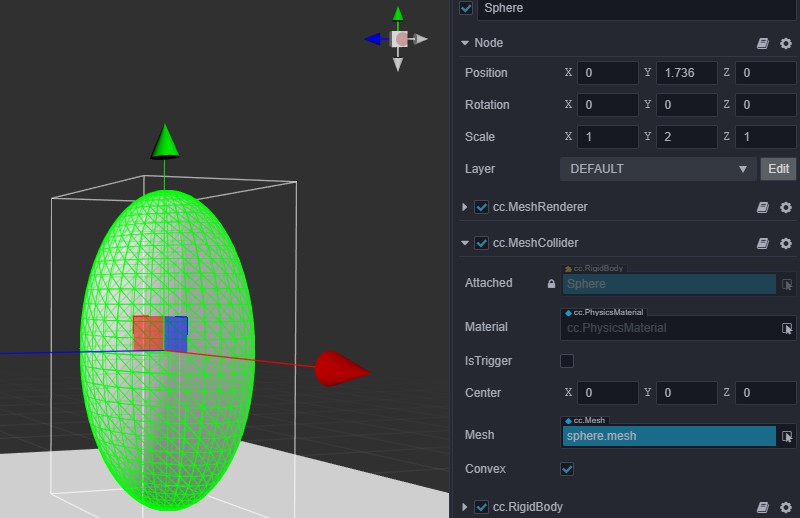
Non-standard Shapes
For non-standard shapes like pebbles, you can use MeshCollider to replace the base colliders.
Note: If you need to support kinmetaic rigid bodies, you must enable the convex function.
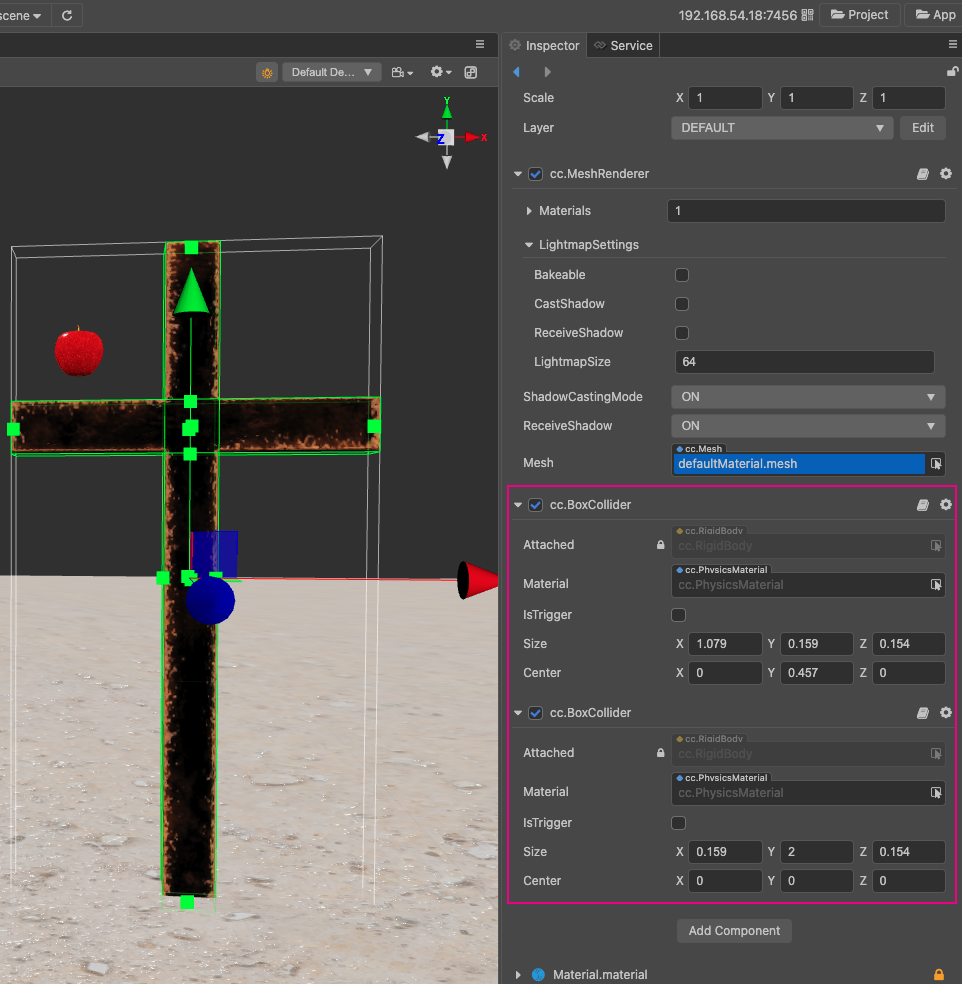
Composite Colliders
For a single node it is easy to see if there is a physical element, but in the case of a node chain (a physical element consisting of a tree of nodes) it is difficult to see which nodes and which components the physical element is composed of.
For the case of node chains, there are currently two usage options.
Each node in the node chain is an element as long as it has a physical component, so that there is no dependency between the components of the parent and child nodes. If the node needs more than one collider shape, just add the corresponding Collider component to that node.
Disadvantages:
- Hierarchical structure is not intuitive enough, multiple shapes can only be added to one node, while displaying shapes requires adding sub-node models and makes it difficult to support local rotation of collision bodies.
- When adjusting the parameters of the node chain, two places need to be adjusted at the same time: the position information of the child nodes and the data information of the corresponding Collider component on the parent node.
If you find a RigidBody component, you bind your own Collider component to that node, otherwise the Collider components in the whole chain will share a single RigidBody component, and the node corresponding to the element is the node corresponding to the top-level Collider component.
Disadvantages:
- Increases node coupling, and when nodes are updated, the corresponding dependent nodes need to be updated.
- More content needs to be maintained when the node chain is broken, and the node chain needs to handle complex logic when it is repeatedly broken.
Note: Currently Cocos Creator is using scheme 1, subsequent versions may also be adjusted, please pay attention to the version update announcement.
