MeshRenderer Component Reference
The MeshRenderer component is used to display a static 3D model. Set the model mesh with the Mesh property, and change the appearance of the model with the Materials property.
Click Add Component -> Mesh -> MeshRenderer in the Inspector panel to add the MeshRenderer component.
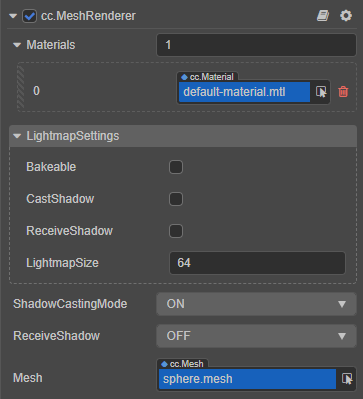
MeshRenderer Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Materials | The material used to render the model, one material corresponds to one sub-mesh in the mesh. |
| LightmapSettings | For baking Lightmap, please refer to Lightmapping for details. |
| ShadowCastingMode | Specifies whether the current model will cast shadows, which needs to enable shadow effect in the scene first |
| ReceiveShadow | Specifies whether the current model will receive and display shadow effects generated by other objects, which needs to enable shadow effect in the scene first. This property takes effect only when the shadow type is ShadowMap. |
| Mesh | 3D model assets for rendering. |
The component interfaces for the common model are described in MeshRenderer API.
The component interfaces for the skinning model are described in SkinnedMeshRenderer API.
Mesh Assets
Mesh assets are necessary for rendering meshes. Currently, meshes are mainly generated automatically by Creator when importing models into Creator.
A Mesh asset contains a set of vertices and multiple sets of indices. The index points to the vertex in the vertex array, and every three sets of indices form a triangle. A mesh is composed of multiple triangles and is the most basic graphical element in the 3D world. Multiple triangles are stitched together to form a complex polygon, and multiple polygons are stitched together to form a 3D model.
Creator provides several simple static 3D models with basic models such as the cube, cylinder, etc. Developers can create a few in the Hierarchy panel as needed to get a first look.
Model Group Rendering
The group rendering function is determined by the Visibility property of the camera component and the Layer property of the node. Users can set the Visibility value through code to complete the group rendering. All nodes belong to the DEFAULT layer by default and are visible on all cameras.
Static Batching
The current static batching scheme is static batching at run time. Static batching can be performed by calling BatchingUtility.batchStaticModel. This function receives a node, and then merges all Mesh in MeshRenderer under that node into one, and hangs it under another node.
After batching, the original transform of MeshRenderer cannot be changed, but the transform of the root node after batching can be changed. Only nodes that meet the following conditions can be statically batched:
- The child node can only contain
MeshRenderer. - The vertex data structure of
MeshofMeshRendererunder child nodes must be consistent. - The material of
MeshRendererunder child nodes must be the same.
Dynamic Batching
The engine currently provides instancing batching .
To turn on batching, simply check the corresponding USE_INSTANCING switch in the material used by the model.
Note: the current batching process introduces several limitations:
- The transparent models in the same batch are not sorted, this may lead to incorrect blending results.
- The inverse-transpose world matrix is not uploaded into batches, models with non-uniform scale will have inaccurate normals.
- Only plain models and skinning models under pre-baked skeletal animation are supported. (i.e. real-time skeletal animations, 2D objects, UIs and particles do not support dynamic batching)
Instancing Batching
The batch through instancing is suitable for drawing a large number of dynamic models with the same vertex data. When enabled, drawing will be grouped according to the material and vertex data, and the instanced attributes information will be organized in each group, and then complete the drawing at one time.
Note: for the support and related settings of the skinning model, refer to the Skeletal Animation Component documentation.
In addition, inside each group, the instanced attributes supports custom additional instanced attributes, which can pass more per-instance data between different instances (such as the difference in appearance of a diffuse color between different characters, or the influence of wind in a large grass field). This requires the support of custom effects. For more detailed instructions, please refer to the Syntax Guide documentation.
VB-merging Batching
VB-merging batching will do some operations such as merging vertices per frame introduce a portion of CPU overhead, which is particularly expensive in JavaScript. Abuse without rigorous testing can cause performance degradation, This feature has been removed in 3.6.2, so please use Instancing or static batching as a preference instead.
In addition, it is necessary to remind that . Optimal performance is often the result of CPU and GPU load balancing, so when using batch functions, be sure to do more tests to identify performance bottlenecks and do targeted optimization.
Batch Best Practices
Generally speaking, the priority of the batch system is: static batching -> instancing batching.
The material must be insured that it is consistent, under this premise:
- If you are certain that certain models will remain completely static during the game cycle, use static batching.
- If there are a large number of the same model repeated drawing, there is only a relatively controllable small difference between each other, use instancing batching.
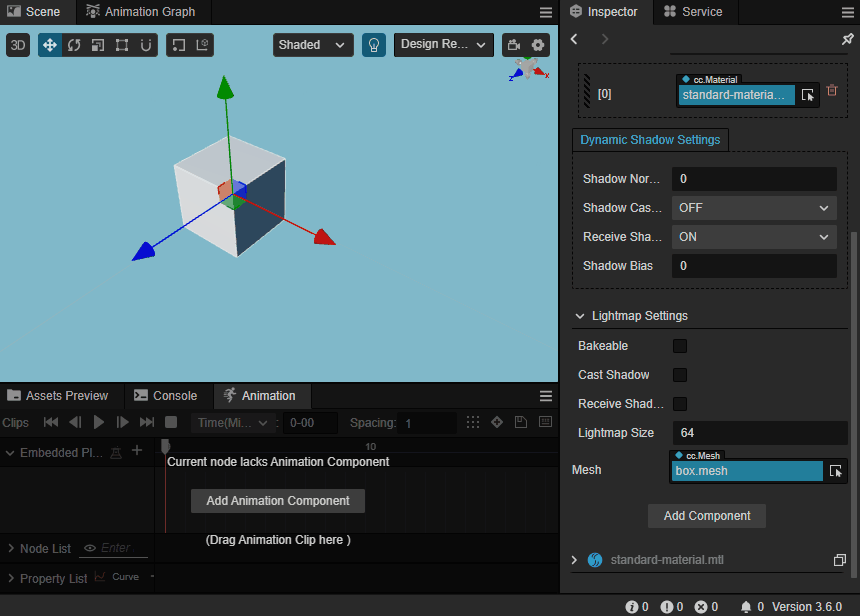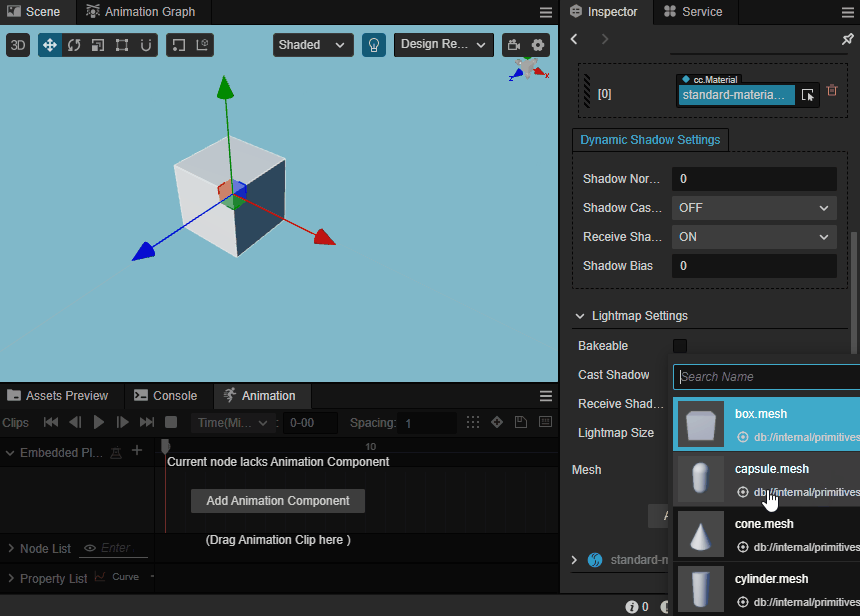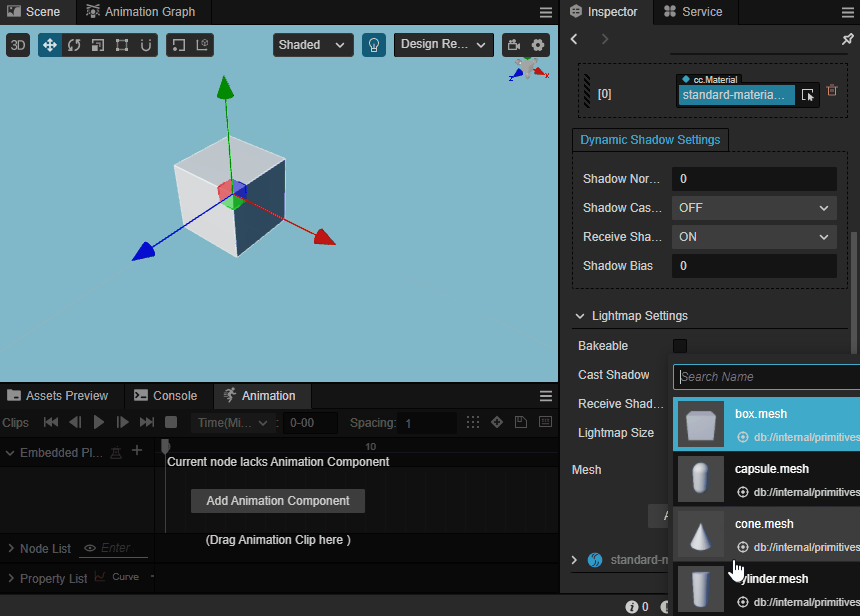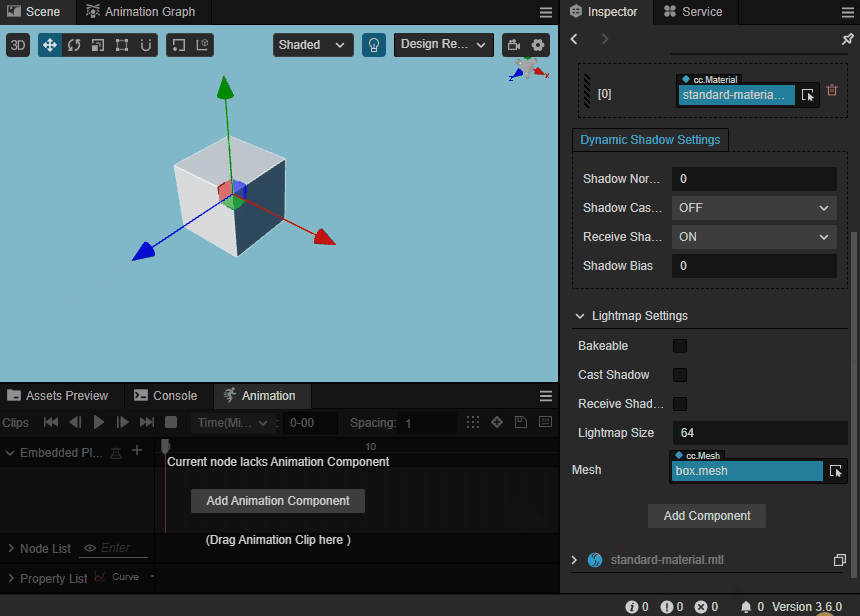
Preview Model
The model can be observed in the scene view when the mouse hovers over the drop-down mesh in the Mesh property.
[^1]: Currently use uniforms to upload the batched world transformation matrix, taking into account the WebGL standard uniform quantity limit, the current batch draws up to 10 models, so for a large number of same For the material model, the number of drawcalls is expected to be reduced by up to 10 times after enabling VB-merging batching. [^2]: There have been many discussions in the industry on the topic of batching and performance, you can refer to this nVidia slide.
